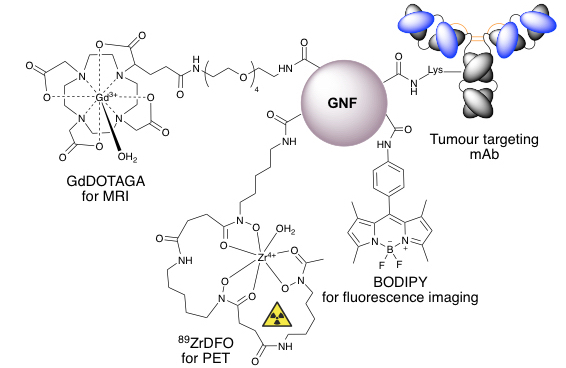
Graphene nanoflake antibody conjugates for multi-modal imaging
Graphene nanoflakes (GNFs) consist of a graphene sheet approximately 30 nm in diameter with a pristine aromatic system and an edge terminated with carboxylic acid groups.[1,2] The high water solubility, negative zeta potential, and relative ease of functionalisation using carboxylate chemistry means that GNFs are ideal scaffolds for multi-functionalisation. Our previous work demonstrated that GNFs can be loaded with the Glu-NH-C(O)-NH-Lys prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding motif, a potent anti-mitotic drug (R)-ispinesib, and the chelate desferrioxamine B (DFO), to create theranostic agents.[3] Here, GNFs were functionalised with a variety of compounds including GdDOTAGA for MRI imaging, DFO for 89Zr-radiolabelling for positron emission tomography imaging and BODIPY for fluorescent imaging. Constructs were tagged to the tumour targeting mAb, trastuzumab, creating a biological targeted platform for fluorescence and PET/MR imaging.
Amide coupling chemistry was successfully adapted to functionalise the GNFs with DFO, GdDOTAGA or BODIPY. Functionalised GNFs were purified on silica gel and then coupled to trastuzumab using EDC/NHS. Fluorescence assisted cell sorting (FACS) analysis using the fluorescent BODIPY-GNF-mAb construct indicated that cells selectively bind to HER2/neu expressing cell lines. A 2.5-fold increased uptake in the SKOV-3 cell line was seen in BODIPY-GNF-mAb compared to BODIPY-GNF, confirming that the GNF does not prevent binding to the target HER2/neu. The DFO-GNF-mAb construct was radiolabelled with 89Zr (RCY = 27.6%, isolated RCP = 86.4%) and subsequent Lindmo cellular assay indicated binding to SKOV-3 cells with immunoreactivity of 35.7±8.0%. Preliminary PET imaging in athymic nude mice bearing a subcutaneous SKOV-3 tumour, indicated significant tumour uptake. A DFO-DOTAGA-GNF-mAb construct has also been synthesised. Radiolabelling, cellular assays and in vivo imaging will evaluate the potential of the construct as a multi-modality PET/MR imaging agent.
[1] C. G. Salzmann and M. L. H. Green, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 314–319.
[2] M. Rosillo-lopez, J. Lee, M. Bella, M. Hart and C. G. Salzmann, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 104198–104202.
[3] J. Lamb, E. Fischer, M. Rosillo-Lopez, C. G. Salzmann and J. P. Holland, Chem. Sci., 2019,10, 8880-8888