Discovery and optimization of novel LpxC inhibitors for the treatment of serious Gram-negative infections
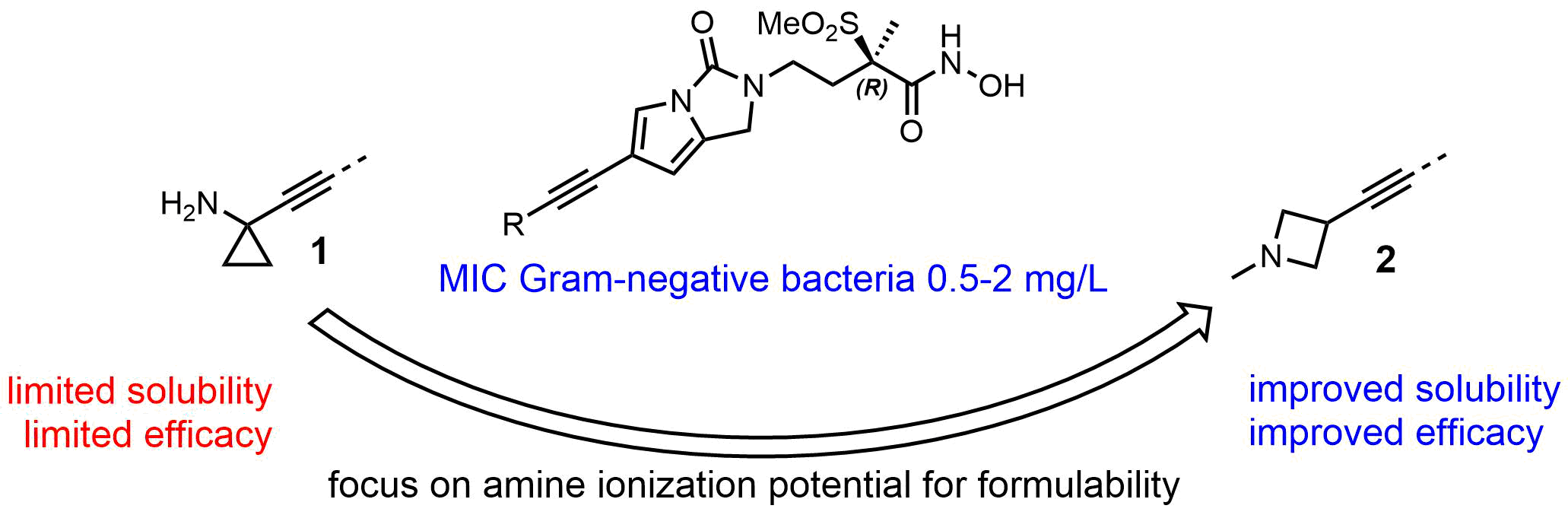
UDP-3-O-((R)-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-glucosamine deacetylase (LpxC) is as an attractive target for the discovery and development of novel antibacterial drugs addressing multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. After the discovery of novel inhibitors of LpxC, featuring a methylsulfone hydroxamic acid warhead harnessed on a 1,2-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[1,2-c]imidazole-3-one scaffold, a structure-based lead generation afforded bis-alkyne compounds such as 1 with decent in vitro potency. However, their solubility and efficacy in vivo remained limited. The lead optimization program resulted eventually in the identification of a series of azetidines with high solubility and potent efficacy against Gram-negative pathogens in animal infection models. The presentation will describe the discovery of compound 1 and the dedicated optimization process that led to compound 2.[1,2]
[1] Surivet, J-P. et al, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 66-87
[2] Panchaud, P. et al, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 88-102