Zooming in on the O-O Bond Formation – Novel Insights from ab initio Molecular Dynamics with Enhanced Sampling Techniques
The process of splitting water into molecular hydrogen and oxygen is among the most promising approaches in the field of renewable energy sources. In order to make this reaction economically viable, in-depth understanding of the crucial O-O bond formation is highly desirable. In the past we have studied a family of Ru-based water oxidation catalysts (WOCs) bearing a Py5 ligand by means of geometry optimization based simulation protocols employing density functional theory (DFT).[1,2] In our current studies we go beyond the static description of the reactive intermediates by utilizing forefront enhanced sampling techniques such as the Bluemoon ensemble and metadynamics together with high-performance DFT-based molecular dynamics simulations.
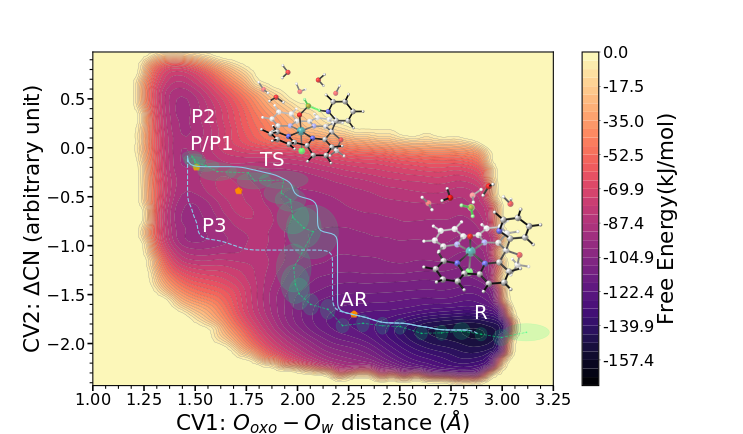
In doing so, we can more accurately describe solute-solvent interactions as well as the dynamics of the system at ambient temperature. This allows us to get detailed insights into the process of the oxygen-oxygen bond formation event, the associated reaction network, and the flexibility of the product state. Moreover, we demonstrate how crucial the choice of an appropriate collective variable is in order to capture the relevant features of the studied reaction.[3]
Lately, we have applied the developed simulation protocol to investigate the influence of the base-strength onto the O-O bond formation event. To this extent we study a modified version of the Py5 ligand that was proposed earlier in an in silico design study, the goal of which was to improve the catalytic performance of those Ru-based WOCs.[2] In short, we find that increasing the basicity of the intramolecular base facilitates a water nucleophilic attack mechanism by altering the solvation shell of the catalysts. This clearly shows how important an adequate description of environmental effects and solute-solvent interactions is.[4]
[1] Gil-Sepulcre et al. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4517.
[2] Schilling, Böhler and Luber, Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 10480.
[3] Schilling, Cunha and Luber, JCTC 2020, 16, 2436-2449.
[4] Schilling, Cunha and Luber, ACS Catal. 2020 in revision.